category
本文由CrewAI的Joao Moura和Tony Kipkenboi合著。
随着智能体系统从实验工具向关键任务业务资产的过渡,企业人工智能领域正在发生翻天覆地的变化。到2025年,人工智能代理预计将成为业务运营不可或缺的一部分,德勤预测,25%使用生成式人工智能的企业将部署人工智能代理,到2027年将增长到50%。全球人工智能代理空间预计将从2024年的51亿美元激增到2030年的471亿美元,反映了这些技术的变革潜力。
在这篇文章中,我们将探讨CrewAI的开源智能体框架如何与Amazon Bedrock相结合,创建复杂的多智能体系统,从而改变企业的运营方式。通过实例和实现细节,我们演示了如何构建、部署和编排AI智能体,这些智能体可以在最少的人为监督下处理复杂的任务。尽管“智能体”是2025年的流行语,但重要的是要了解什么是人工智能智能体,以及部署智能体系统可以在哪里产生好处。
智能体设计
人工智能智能体是一个自主的智能系统,它使用大型语言模型(LLM)和其他人工智能功能,在最少的人为监督下执行复杂的任务。与遵循预定义规则的传统软件不同,人工智能智能体可以独立操作,从环境中学习,适应不断变化的条件,并做出上下文决策。它们采用模块化组件设计,如推理引擎、内存、认知技能和工具,使其能够执行复杂的工作流程。传统的SaaS解决方案是为横向可扩展性和通用性而设计的,这使得它们适合管理跨不同部门的重复任务,但它们往往缺乏特定领域的智能和灵活性,无法应对动态环境中的独特挑战。另一方面,智能体系统旨在通过将上下文感知系统的灵活性与领域知识相结合来弥合这一差距。考虑一个软件开发用例,人工智能智能体可以生成、评估和改进代码,将软件工程师的重点从常规编码转移到更复杂的设计挑战上。例如,对于CrewAI git存储库,拉取请求由一组CrewAI智能体进行评估,这些智能体根据代码文档、实现的一致性和安全考虑因素审查代码。另一个用例可以在供应链管理中看到,传统的库存系统可能会跟踪库存水平,但缺乏根据行业见解预测供应链中断或优化采购的能力。相比之下,智能体系统可以使用实时数据(如天气或地缘政治风险)来主动重新路由供应链和重新分配资源。下图描述了智能体AI系统的组件:
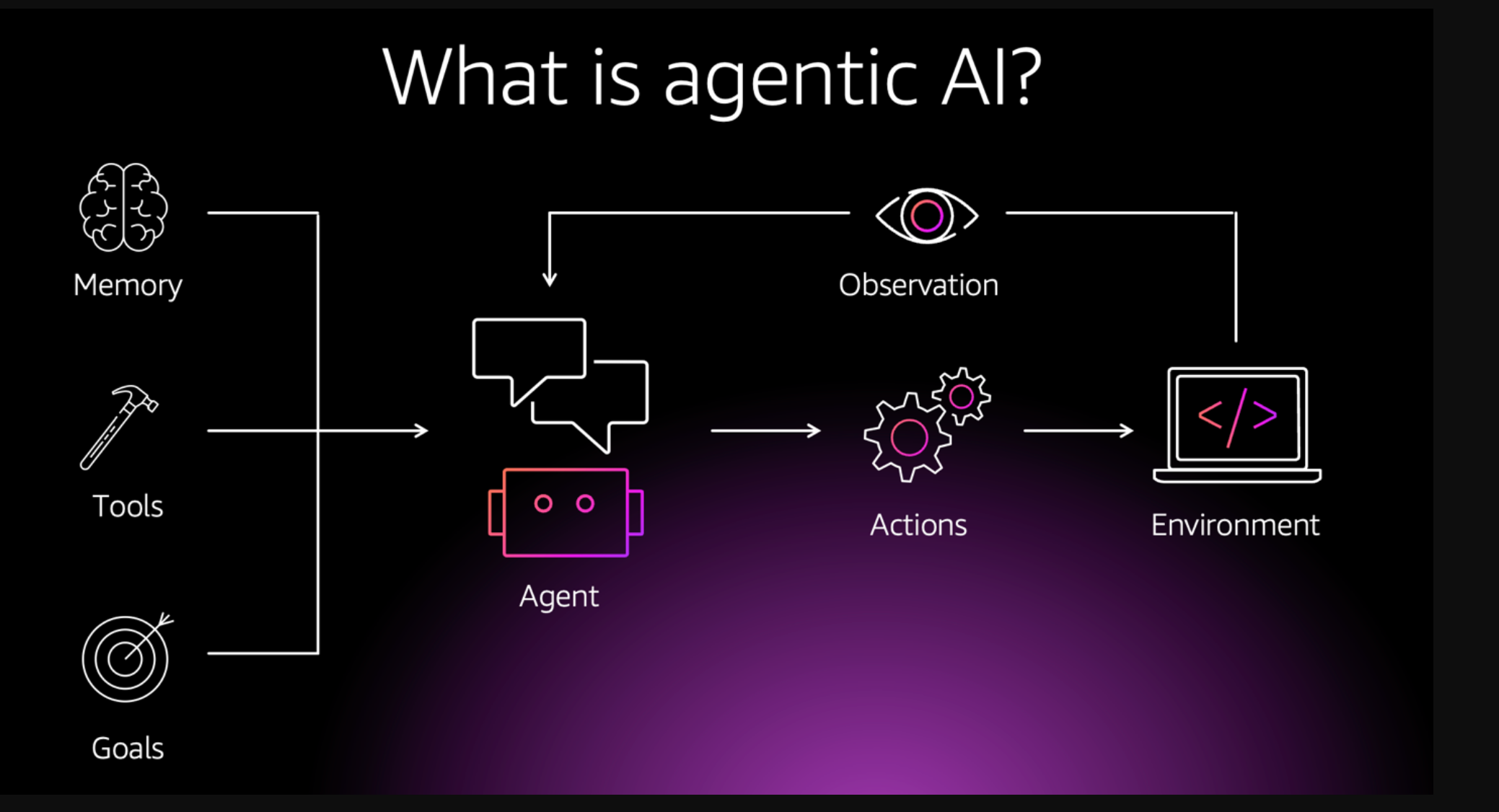
Overview of CrewAI
CrewAI is an enterprise suite that includes a Python-based open source framework. It simplifies the creation and management of AI automations using either AI flows, multi-agent systems, or a combination of both, enabling agents to work together seamlessly, tackling complex tasks through collaborative intelligence. The following figure illustrates the capability of CrewAI’s enterprise offering:
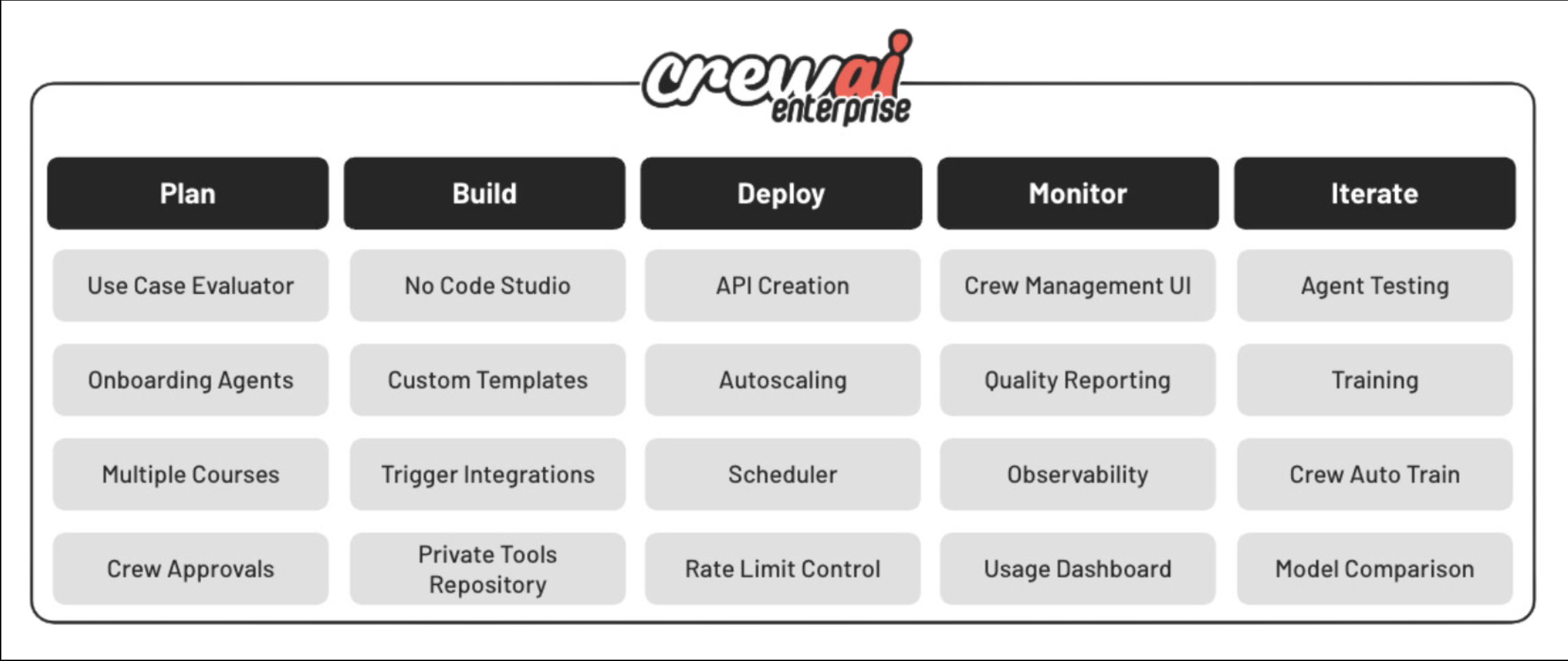
CrewAI’s design centers around the ability to build AI automation through flows and crews of AI agents. It excels at the relationship between agents and tasks, where each agent has a defined role, goal, and backstory, and can access specific tools to accomplish their objectives. This framework allows for autonomous inter-agent delegation, where agents can delegate tasks and inquire among themselves, enhancing problem-solving efficiency. This growth is fueled by the increasing demand for intelligent automation and personalized customer experiences across sectors like healthcare, finance, and retail.
CrewAI’s agents are not only automating routine tasks, but also creating new roles that require advanced skills. CrewAI’s emphasis on team collaboration, through its modular design and simplicity principles, aims to transcend traditional automation, achieving a higher level of decision simplification, creativity enhancement, and addressing complex challenges.
CrewAI key concepts
CrewAI’s architecture is built on a modular framework comprising several key components that facilitate collaboration, delegation, and adaptive decision-making in multi-agent environments. Let’s explore each component in detail to understand how they enable multi-agent interactions.
At a high level, CrewAI creates two main ways to create agentic automations: flows and crews.
Flows
CrewAI Flows provide a structured, event-driven framework to orchestrate complex, multi-step AI automations seamlessly. Flows empower users to define sophisticated workflows that combine regular code, single LLM calls, and potentially multiple crews, through conditional logic, loops, and real-time state management. This flexibility allows businesses to build dynamic, intelligent automation pipelines that adapt to changing conditions and evolving business needs. The following figure illustrates the difference between Crews and Flows:
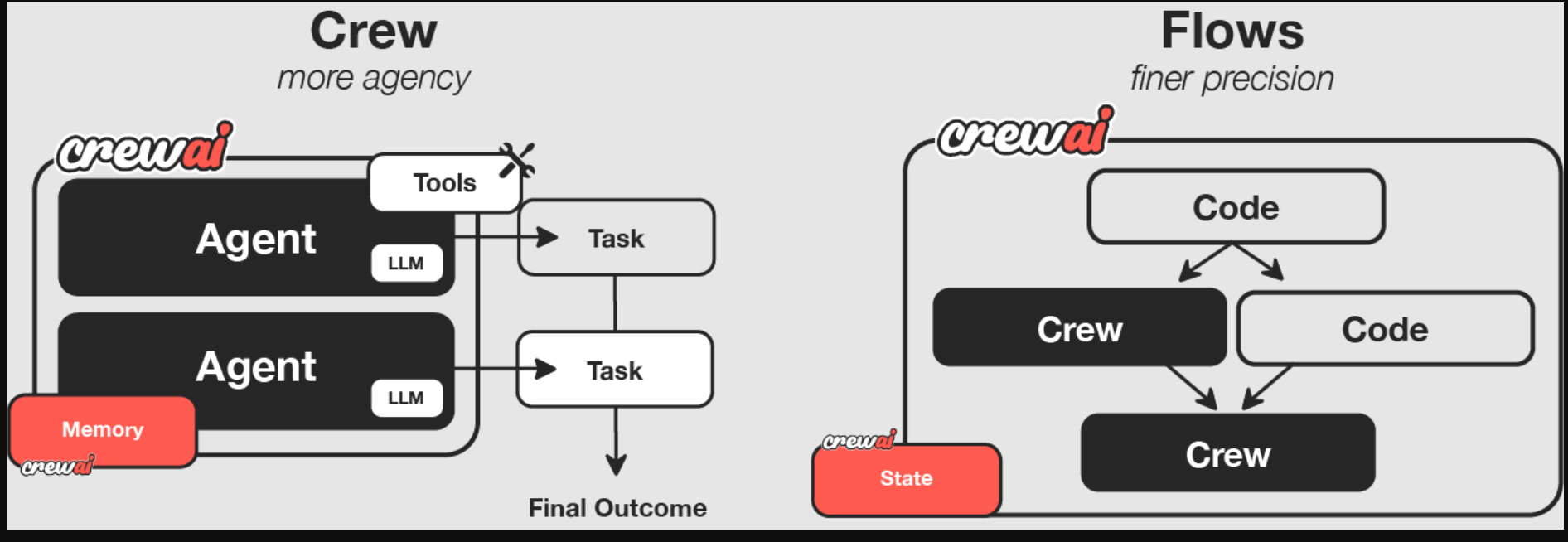
When integrated with Amazon Bedrock, CrewAI Flows unlock even greater potential. Amazon Bedrock provides a robust foundation by enabling access to powerful foundation models (FMs).
For example, in a customer support scenario, a CrewAI Flow orchestrated through Amazon Bedrock could automatically route customer queries to specialized AI agent crews. These crews collaboratively diagnose customer issues, interact with backend systems for data retrieval, generate personalized responses, and dynamically escalate complex problems to human agents only when necessary.
Similarly, in financial services, a CrewAI Flow could monitor industry conditions, triggering agent-based analysis to proactively manage investment portfolios based on industry volatility and investor preferences.
Together, CrewAI Flows and Amazon Bedrock create a powerful synergy, enabling enterprises to implement adaptive, intelligent automation that addresses real-world complexities efficiently and at scale.
Crews
Crews in CrewAI are composed of several key components, which we discuss in this section.
Agents
Agents in CrewAI serve as autonomous entities designed to perform specific roles within a multi-agent system. These agents are equipped with various capabilities, including reasoning, memory, and the ability to interact dynamically with their environment. Each agent is defined by four main elements:
- Role – Determines the agent’s function and responsibilities within the system
- Backstory – Provides contextual information that guides the agent’s decision-making processes
- Goals – Specifies the objectives the agent aims to accomplish
- Tools – Extends the capabilities of agents to access more information and take actions
Agents in CrewAI are designed to work collaboratively, making autonomous decisions, delegating tasks, and using tools to execute complex workflows efficiently. They can communicate with each other, use external resources, and refine their strategies based on observed outcomes.
Tasks
Tasks in CrewAI are the fundamental building blocks that define specific actions an agent needs to perform to achieve its objectives. Tasks can be structured as standalone assignments or interdependent workflows that require multiple agents to collaborate. Each task includes key parameters, such as:
- Description – Clearly defines what the task entails
- Agent assignment – Specifies which agent is responsible for executing the task
Tools
Tools in CrewAI provide agents with extended capabilities, enabling them to perform actions beyond their intrinsic reasoning abilities. These tools allow agents to interact with APIs, access databases, execute scripts, analyze data, and even communicate with other external systems. CrewAI supports a modular tool integration system where tools can be defined and assigned to specific agents, providing efficient and context-aware decision-making.
Process
The process layer in CrewAI governs how agents interact, coordinate, and delegate tasks. It makes sure that multi-agent workflows operate seamlessly by managing task execution, communication, and synchronization among agents.
More details on CrewAI concepts can be found in the CrewAI documentation.
CrewAI enterprise suite
For businesses looking for tailored AI agent solutions, CrewAI provides an enterprise offering that includes dedicated support, advanced customization, and integration with enterprise-grade systems like Amazon Bedrock. This enables organizations to deploy AI agents at scale while maintaining security and compliance requirements.
Enterprise customers get access to comprehensive monitoring tools that provide deep visibility into agent operations. This includes detailed logging of agent interactions, performance metrics, and system health indicators. The monitoring dashboard enables teams to track agent behavior, identify bottlenecks, and optimize multi-agent workflows in real time.
Real-world enterprise impact
CrewAI customers are already seeing significant returns by adopting agentic workflows in production. In this section, we provide a few real customer examples.
Legacy code modernization
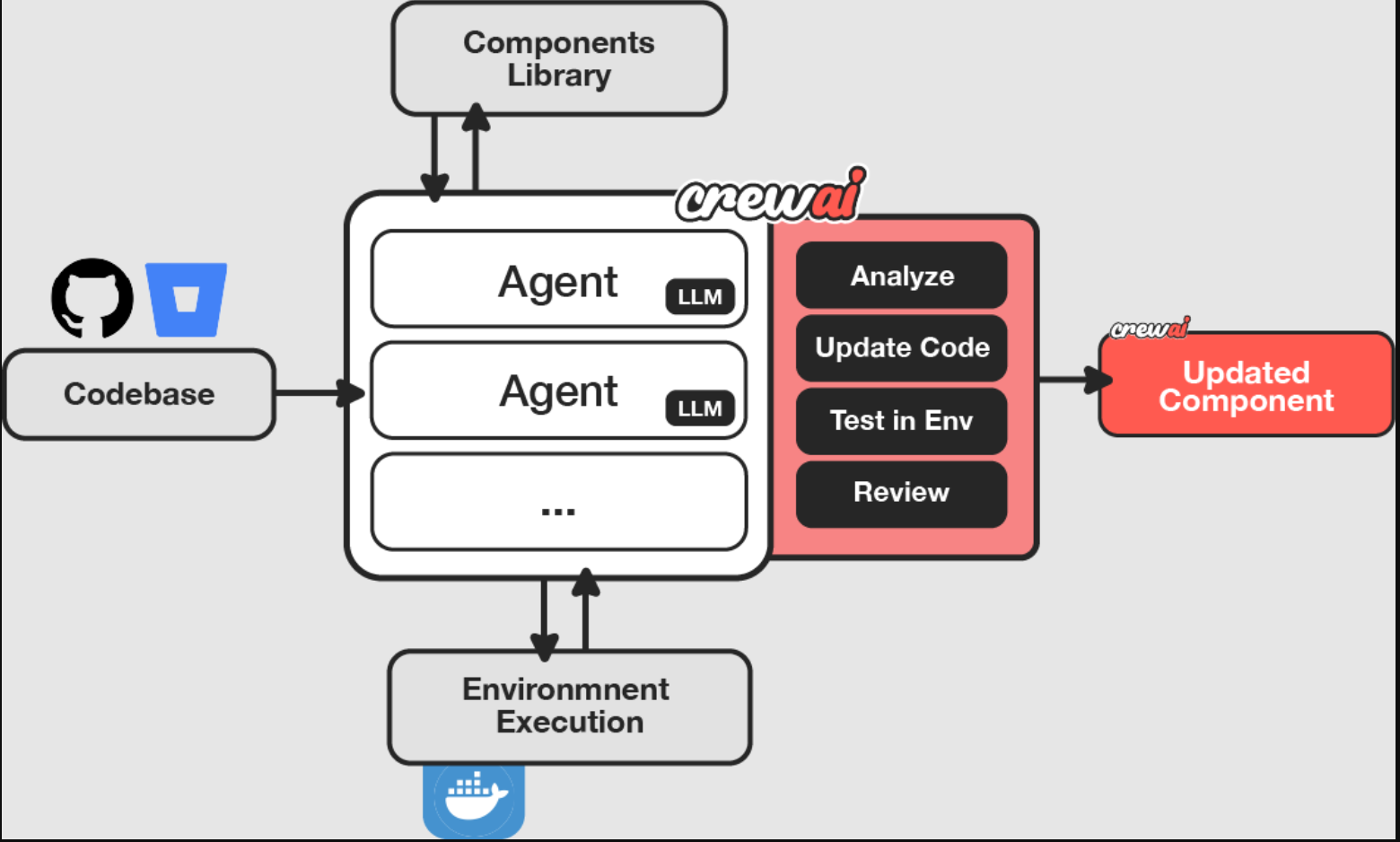
A large enterprise customer needed to modernize their legacy ABAP and APEX code base, a typically time-consuming process requiring extensive manual effort for code updates and testing.
Multiple CrewAI agents work in parallel to:
- Analyze existing code base components
- Generate modernized code in real time
- Execute tests in production environment
- Provide immediate feedback for iterations
The customer achieved approximately 70% improvement in code generation speed while maintaining quality through automated testing and feedback loops. The solution was containerized using Docker for consistent deployment and scalability. The following diagram illustrates the solution architecture.
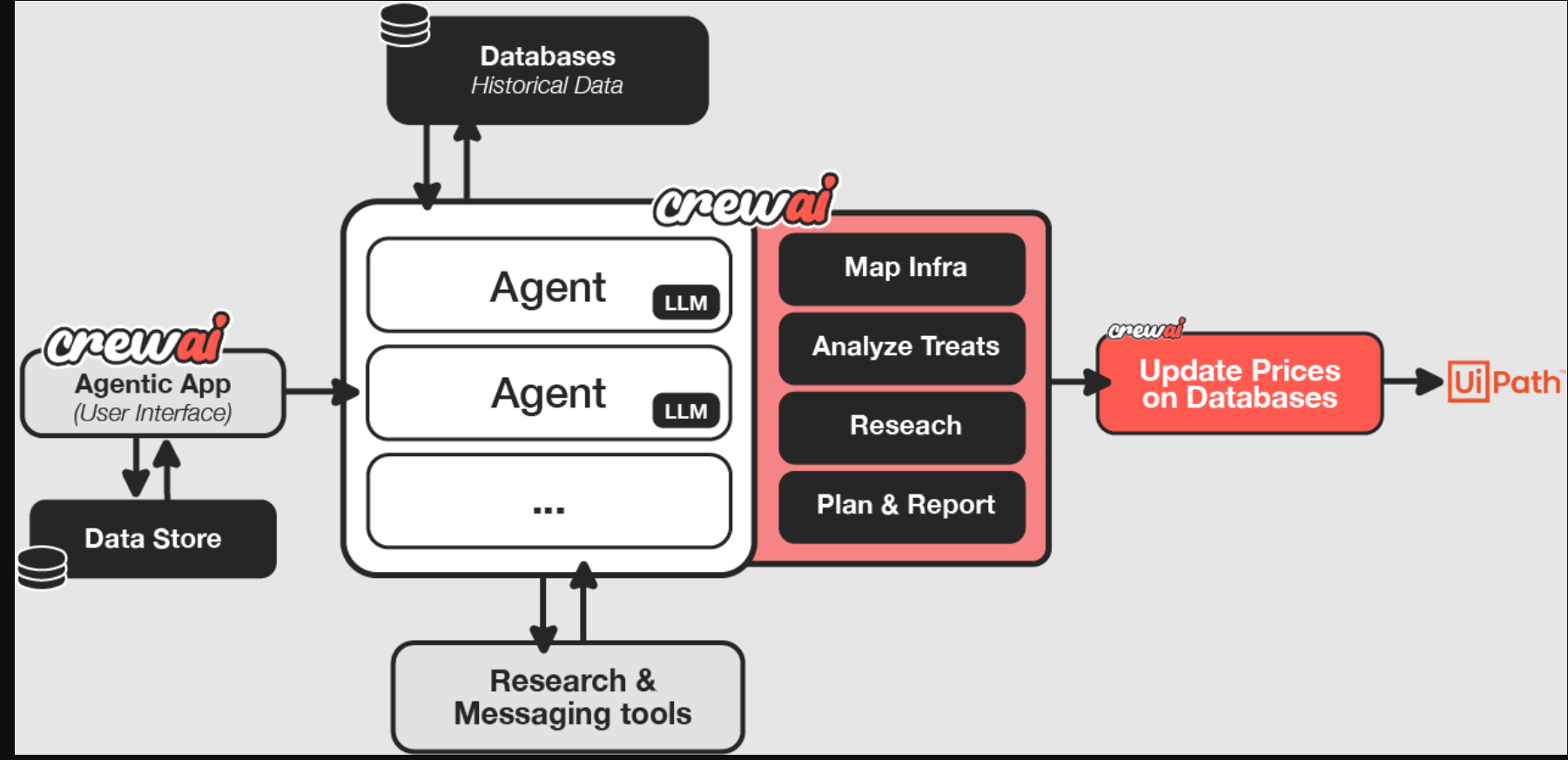
Back office automation at global CPG company
A leading CPG company automated their back-office operations by connecting their existing applications and data stores to CrewAI agents that:
- Research industry conditions
- Analyze pricing data
- Summarize findings
- Execute decisions
The implementation resulted in a 75% reduction in processing time by automating the entire workflow from data analysis to action execution. The following diagram illustrates the solution architecture.
Get started with CrewAI and Amazon Bedrock
Amazon Bedrock integration with CrewAI enables the creation of production-grade AI agents powered by state-of-the-art language models.
The following is a code snippet on how to set up this integration:
Check out the CrewAI LLM documentation for detailed instructions on how to configure LLMs with your AI agents.
Amazon Bedrock provides several key advantages for CrewAI applications:
- Access to state-of-the-art language models such as Anthropic’s Claude and Amazon Nova – These models provide the cognitive capabilities that power agent decision-making. The models enable agents to understand complex instructions, generate human-like responses, and make nuanced decisions based on context.
- Enterprise-grade security and compliance features – This is crucial for organizations that need to maintain strict control over their data and enforce compliance with various regulations.
- Scalability and reliability backed by AWS infrastructure – This means your agent systems can handle increasing workloads while maintaining consistent performance.
Amazon Bedrock Agents and Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases as native CrewAI Tools
Amazon Bedrock Agents offers you the ability to build and configure autonomous agents in a fully managed and serverless manner on Amazon Bedrock. You don’t have to provision capacity, manage infrastructure, or write custom code. Amazon Bedrock manages prompt engineering, memory, monitoring, encryption, user permissions, and API invocation. BedrockInvokeAgentTool enables CrewAI agents to invoke Amazon Bedrock agents and use their capabilities within your workflows.
With Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases, you can securely connect FMs and agents to your company data to deliver more relevant, accurate, and customized responses. BedrockKBRetrieverTool enables CrewAI agents to retrieve information from Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases using natural language queries.
The following code shows an example for Amazon Bedrock Agents integration:
The following code shows an example for Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases integration:通过AWS上的CrewAI进行监控、跟踪和可观察性,实现卓越运营
与任何软件应用程序一样,在生产环境中部署智能体应用程序时,实现卓越运营至关重要。这些应用程序是复杂的系统,包括顺序或并行交互的确定性和概率性组件。因此,全面监控、可追溯性和可观察性是实现卓越运营的关键因素。这包括三个关键方面:
应用程序级可观察性——提供整个系统的平稳运行,包括智能体编排框架CrewAI和潜在的其他应用程序组件(如前端)
模型级可观察性——提供可靠的模型性能(包括准确性、延迟、吞吐量等指标)
智能体级可观察性——在单智能体或多智能体系统中保持高效运行
在AWS上使用CrewAI和Amazon Bedrock运行基于智能体的应用程序时,您可以访问这些维度的一套全面的内置功能:
- 应用程序级日志–Amazon CloudWatch会自动从您在所选AWS计算平台(如AWS Lambda、Amazon Elastic Container Service(Amazon ECS)或Amazon Elastics compute Cloud(Amazon EC2))上运行的应用程序代码中收集应用程序级日志和指标。CrewAI框架提供应用程序级日志记录,默认情况下配置为最低级别。为了获得更详细的见解,可以在初始化期间通过设置verbose=True在智能体或团队级别启用详细日志记录。
- 模型级调用日志——此外,CloudWatch会自动从Amazon Bedrock收集模型级调用记录和指标。这包括基本的性能指标。
- 智能体级可观察性——CrewAI与流行的第三方监控和可观察性框架无缝集成,如AgentOps、Arize、MLFlow、LangFuse等。这些框架实现了对系统性能的全面跟踪、调试、监控和优化。代理智能体
解决方案概述
云安全态势管理(CSPM)是一项重要功能,通过不断扫描云基础设施的配置错误和合规风险,为组织提供全面的云安全状态视图。
传统的安全评估通常需要多名专家、协调的时间表和无数的人工检查。使用CrewAI智能体,您可以简化整个过程,自动映射资源,分析配置,并生成清晰、优先的补救步骤。
下图说明了解决方案架构。
我们的用例演示实现了一个由三名智能体组成的专门团队,每个智能体都有不同的职责,与您在专业安全咨询公司中可能遇到的角色相呼应:
- 基础设施映射器——充当我们的系统架构师
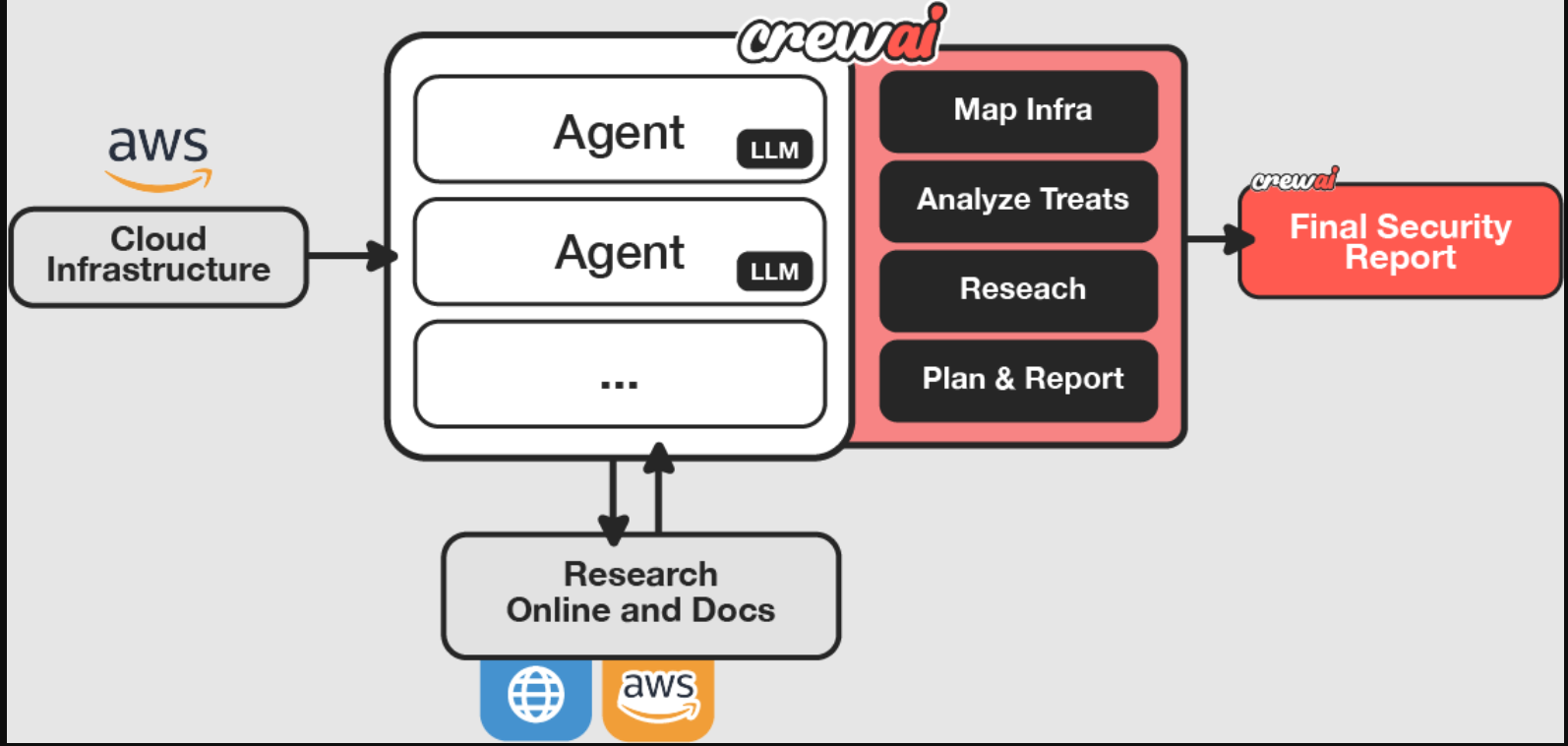 ,有条不紊地记录AWS资源及其配置。与经验丰富的云架构师一样,它创建了一个详细的清单,作为我们安全分析的基础。
,有条不紊地记录AWS资源及其配置。与经验丰富的云架构师一样,它创建了一个详细的清单,作为我们安全分析的基础。 - 安全分析师——担任我们的网络安全专家,检查基础设施图中的潜在漏洞,并研究当前的最佳实践。它带来了对安全威胁和缓解策略的深入了解。
- 报告撰写人——担任我们的技术文档专家,将复杂的发现综合成清晰、可操作的建议。它确保技术见解能够有效地传达给技术和非技术利益相关者。
实施解决方案
在本节中,我们将介绍安全评估多智能体系统的实现。此示例的代码位于GitHub上。请注意,本文并未明确涵盖解决方案的所有代码工件。
Step 1: Configure the Amazon Bedrock LLM
We’ve saved our environment variables in an .env file in our root directory before we pass them to the LLM class:
Step 2: Define agents
These agents are already defined in the agents.yaml file, and we’re importing them into each agent function in the crew.py file:
Step 3: Define tasks for the agents
Similar to our agents in the preceding code, we import tasks.yaml into our crew.py file:
Step 4: Create the AWS infrastructure scanner tool
This tool enables our agents to interact with AWS services and retrieve information they need to perform their analysis:
Step 5: Assemble the security audit crew
Bring the components together in a coordinated crew to execute on the tasks:
Step 6: Run the crew
In our main.py file, we import our crew and pass in inputs to the crew to run:
The final report will look something like the following code:
此实现展示了CrewAI智能体如何协同工作,执行通常需要多名安全专业人员的复杂安全评估。该系统既可扩展又可定制,允许适应特定的安全要求和合规标准。
结论
在这篇文章中,我们演示了如何使用CrewAI和Amazon Bedrock为AWS基础设施构建一个复杂的自动化安全评估系统。我们探索了多个人工智能智能体如何无缝协作,以执行复杂的安全审计,从基础设施映射到漏洞分析和报告生成。通过我们的示例实现,我们展示了CrewAI的框架如何创建专门的智能体,每个智能体都为安全评估过程带来了独特的功能。通过使用Amazon Bedrock与强大的语言模型集成,我们创建了一个可以自主识别安全风险、研究解决方案并生成可操作建议的系统。
我们分享的实例仅展示了CrewAI在Amazon Bedrock上的众多可能应用之一。CrewAI的智能体编排功能和Amazon Bedrock中的高级语言模型相结合,为构建能够应对复杂业务挑战的智能自主系统开辟了许多可能性。
我们鼓励您在GitHub上探索我们的代码,并开始使用CrewAI和Amazon Bedrock构建自己的多智能体系统。无论您是专注于安全评估、流程自动化还是其他用例,这种强大的组合都为您提供了创建复杂的人工智能解决方案所需的工具,这些解决方案可以根据您的需求进行扩展。
- 登录 发表评论
- 37 次浏览